Guide
See also:
- the README file
- our YouTube channel
- and, above all, this series of articles
Brain Annex is conceptually 3 separate open-source products:
- the BrainAnnex python library (which can be pip installed separately, if desired)
- the BrainAnnex web api (primary for the use of the web app, below; but parts of it are fairly generic)
- the BrainAnnex web app , which offers
A) Control Panel / Database Management pages
B) Search and visualization
C) Plugin-driven Content Management Systems
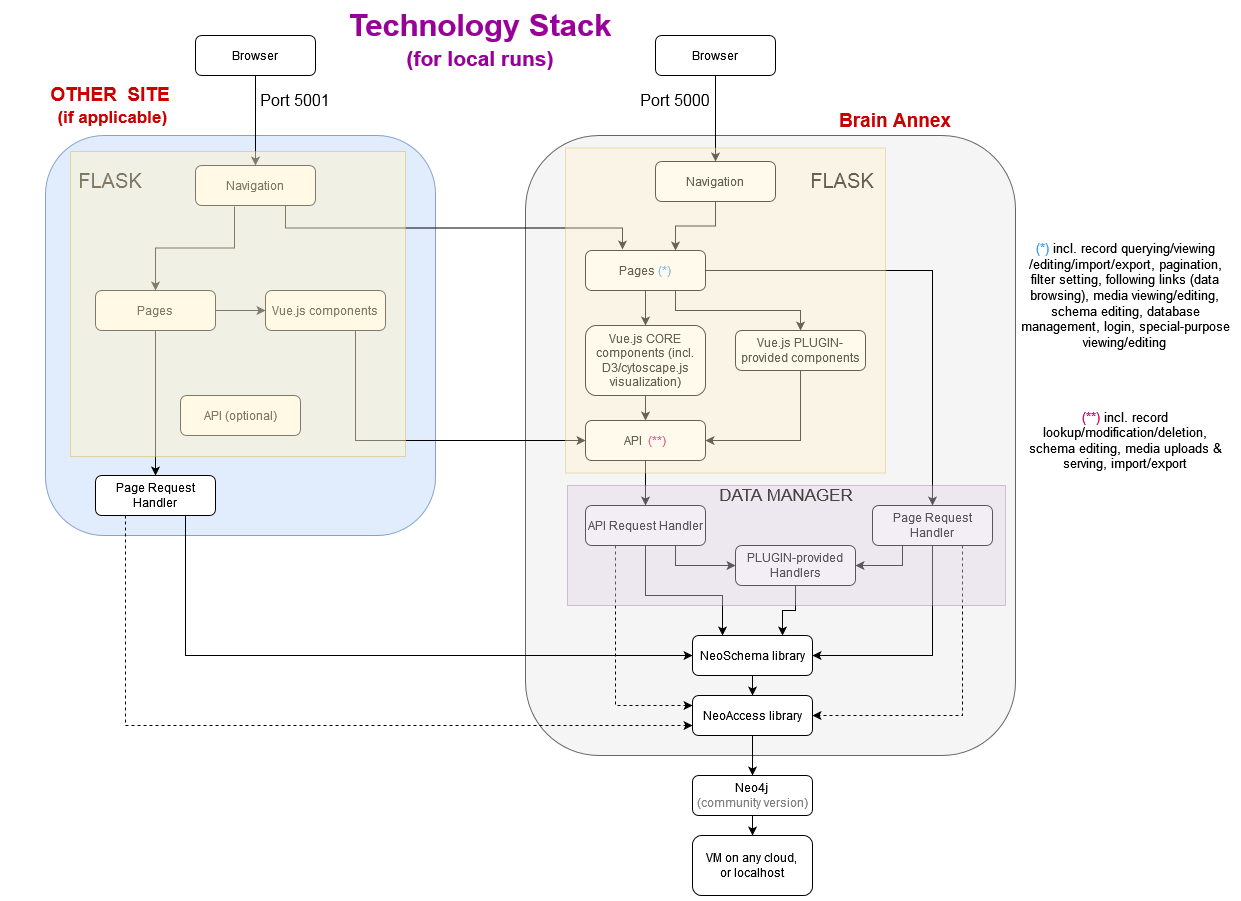
The following Python classes, JavaScript libraries, Flask pages and Vue.js components are being used in the technology stack :
FOUNDATIONAL (CORE) PYTHON LIBRARY
Classes GraphAccess and InterGraph
Classes to interface with the Neo4j graph database (or, potentially, other Cypher-based graph databases) from Python.
There are two parts:
1) "InterGraph": a thin wrapper around the Neo4j python connectivity library Neo4j Python Driver".
This core library allows the execution of arbitrary Cypher (query language) commands,
and helps manage the complex data structures that they return.
It may be used independently, or as the foundation of full "GraphAccess" library.
This bottom layer is dependent on the specific graph database (for operations such as connection, indexes, constraints),
and insulates the higher layers from it.
Currently, 2 versions are available: one for use with the graph database Neo4j v4, and one for Neo4j v5.
More versions, also for Cypher-supporting graph databases other than Neo4j, are anticipated.
2) "GraphAccess" (formerly called "NeoAccess"): A layer above, providing higher-level functionality for common database operations,
such as lookup, creation, deletion, modification, import, etc.
Background Information:
Using Neo4j with Python : the Open-Source Library "GraphAccess"
Reference Guide
Source code
Tutorial 1 Tutorial 2 Tutorial 3 (Pandas import)
Reference Guide
Source code
Tutorial 1 Tutorial 2 Tutorial 3 (Pandas import)
Classes CypherBuilder and CypherUtils Reference Guide
2 helper classes, especially meant for the GraphAccess library, but also for anyone programmatically putting together Cypher queries
Class GraphSchema
(Formerly called "NeoSchema")
A layer above the class GraphAccess (or, in principle, another library providing a compatible interface),
to provide an optional schema to the underlying database.
Schemas may be used to either:
1) acknowledge the existence of typical patterns in the data
OR
2) to enforce a mold for the data to conform to
MOTIVATION
Relational databases are suffocatingly strict for the real world.
Neo4j by itself may be too anarchic.
A schema (whether "lenient/lax/loose" or "strict") in conjunction with Neo4j may be the needed compromise.
GOALS
- Data integrity
- Assist the User Interface
- Infuse into Neo4j functionality that some people turn to RDF for. However, carving out a new path
rather than attempting to emulate RDF!
Background Information:
Using Schema in Graph Databases such as Neo4j
User Guide
Reference Guide
Source code
Tutorial 1 : basic Schema operations (Classes, Properties, Data Nodes)
Tutorial 2 : set up a simple Schema (Classes, Properties) and perform a data import (Data Nodes and relationships among them)
User Guide
Reference Guide
Source code
Tutorial 1 : basic Schema operations (Classes, Properties, Data Nodes)
Tutorial 2 : set up a simple Schema (Classes, Properties) and perform a data import (Data Nodes and relationships among them)
Class Categories
Library for Category-related operations, as well as for management of "Category Pages".
Categories have some attributes, such as "name" and "remarks",
as well as "BA_subcategory" and "BA_see_also" relationships with other categories.
The 1st part of this library handles the above entity.
The 2nd part (possibly to be split off in the future) manages a (for now conflated)
entity of "Category Page", to which a variety of nodes (e.g. representing records or media)
are attached with positional attributes - for example to implement an ordered sequence
of multimedia content on the page of a content-management UI.
Class Collections
An ordered sequence of Data Nodes.
We define a "Collection" as an entity to which a variety of Data Nodes
are attached, with positional attributes in their links.
Example of use case: "pages" of "Content Items" attached to a "Category"
Class FullTextIndexing
Indexing-related methods, for full-text searching
Background Information:
Full-Text Search with the Neo4j Graph Database
Reference Guide
Source code
Tutorial
Reference Guide
Source code
Tutorial
Class UserManager
Class for User Management in the database, including handling of encrypted passwords
Flask Layer : Web API
Class ApiRouting
Setup, routing and endpoints for all the web pages served by this module.
Note that this class does not directly interact with the Neo4j database.
SECTIONS:
- UTILITY methods
- For DEBUGGING
- ROUTING:
* SCHEMA-related (reading)
* SCHEMA-related (creating)
* CONTENT-ITEM MANAGEMENT
VIEWING CONTENT ITEMS
MODIFYING EXISTING CONTENT ITEMS
* CATEGORY-RELATED (incl. adding new Content Items)
POSITIONING WITHIN CATEGORIES
* FILTERS
* IMPORT-EXPORT (upload/download)
* EXPERIMENTAL
Class ServerCommunication (JavaScript)
Static JavaScript class for the front-end to communicate with the server using the fetch() API.
Small wrapper library that simplifies the server communication.
Flask Layer : Web App
Flask serves 2 roles: the implementation of a Web API, and the generation of pages for a web app.
The "Flask" object is instantiated in main.py
The top-level Flask modules that specify how to dispatch the URL's are called "blueprints", and get initialized in main.py, by
calls to several BrainAnnex class methods:
| CLASS METHOD | Prefix for all URL's handled by this module |
|---|---|
| HomeRouting.setup() | (none, i.e. top-level) |
| Navigation.setup() | /navigation |
| PagesRouting.setup() | /BA/pages |
| ApiRouting.setup() | /BA/api |
| SamplePagesRouting.setup() | /sample/pages |
| SampleApiRouting.setup() | /sample/api |
All Flask-related files, except for main.py, are under the flask_modules folder, at the top level.
That includes Pyhon files, Jinja (Flask) templates, and static files (such as CSS, images, JavaScript and Vue.js components)
Python Libraries for the Web App
Class MediaManager
Helper library for the management of media files (documents and images)
Background Information:
A Technology Stack on Top of a (Neo4j) Graph Database
Reference Guide
Source code
Reference Guide
Source code
Class DataManager
For general, high-level database-interaction operations.
Used by the UI for Page Generation,
as well as by the web API to produce data for the endpoints.
This library is primarily a common entry point for data requests:
many specific operations get delegated to other, more specialized, libraries.
This class does NOT get instantiated.
Background Information:
A Technology Stack on Top of a (Neo4j) Graph Database
Reference Guide
Source code
Reference Guide
Source code
Class UploadHelper
Helper class to manage file uploads with Flask 1.1 (using Werkzeug 2.1)
Class DocumentationGenerator
To generate the HTML for a documentation page, from a python file.
Used for the "Reference Guide" pages in this website!
PLUGIN-provided Handlers
Each registered plugin may opt to provide python methods for its specific needs.
Flask Layer : Web-app PAGES
Class PagesRouting
Setup and routing for all the Flask-based web pages served by this module
Class NodeExplorer
A largely experimental library to deal with management and visualization of data nodes
Flask Templates (HTML)
HTML Flask templates for the various pages of the Brain-Annex provided site (including administrative pages and category-viewer pages)
Static Assets (CSS and JavaScript, including Vue.js components)
For the various site pages
Vue.js components
Numerous modules, some utilized by the core program, and others by the modular front-end plugins. All using version 2 of Vue.js
Vue components utilized by the core program:
bread_crumbs , category_navbox , content_items , controls , record_navigator , schema_creator , schema_editor , toc_sidebar
Vue components utilized for visualization:
a group of components in the folder "vue_cytoscape"
Vue components utilized by the modular front-end plugins:
a group of components in the folder "PLUGINS": codedocs , documents , headers ,
image_gallery , images , notes , records , recordsets , site_link , timer
Flask Layer : NAVIGATION
Class Navigation
Router/generator for navigation pages:
CSS static pages, and HTML pages that get included into other Flask files
Setup, and routing, for all the web pages
Function get_site_pages()
Definition of the Navigation Bar entries for the overall site navigation
(both Brain Annex and, possibly, co-hosted sites)
VISUALIZATION
Class DisplayNetwork
Used to create an HTML file that graphically displays an interactive version
of graph-network data
Class PyGraphVisual
Facilitate data preparation for graph visualization that uses the Cytoscape.js library
TOP LEVEL
MAIN PROGRAM
It starts up a server for web User Interface and an API
Run this file, and then set the browser to http://localhost:5000/some_url
(the actual port number is configurable; the URL's are specified in the various modules)
IMPORTANT: first change the config.ini file as needed (for instructions, see the install page)
Note: this main program may also be started from the CLI with the "flask run" command
Class InitializeBrainAnnex
INITIALIZATION of various static classes
CONFIGURATION FILES
The installation comes with a file of default configurations: config.defaults.ini
This file needs to be duplicated, renamed config.ini , and personalized. For instructions, see the install page
Data from this file can be accessed in other modules (such as main.py) by using: from configparser import ConfigParser
Utilities
General utilities for comparisons and pandas